 Image credit: D. Contreras
Image credit: D. ContrerasAbstract
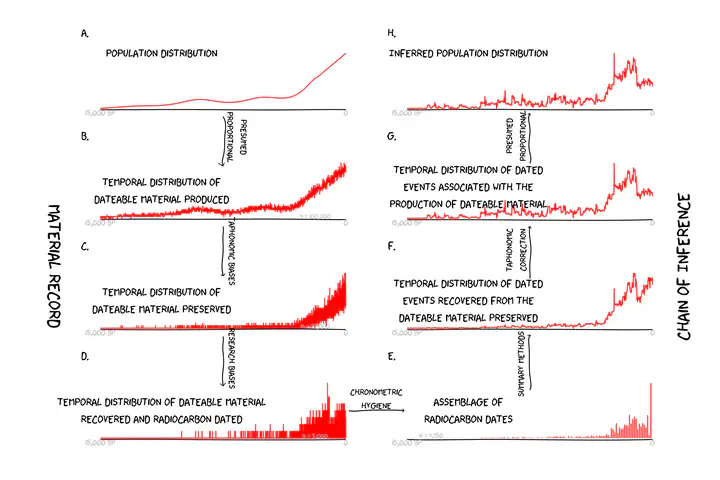
Accurately reconstructing past human population dynamics is critical for explaining major patterns in the human past. Demand for demographic proxies has driven hopeful interest in the “dates-as-data” approach, which models past demography by assuming a relationship between population size, the production of dateable material, and the corpus of radiocarbon dates produced by archaeological research. However, several biases can affect assemblages of dates, complicating inferences about population size. One serious but potentially addressable issue centers on landscape taphonomy — the ways in which geologic processes structure the preservation and recovery of archaeological sites and/or materials at landscape scales. Here, we explore the influence of landscape taphonomy on demographic proxies. More specifically, we evaluate how well demographic proxies may be corrected for taphonomic effects with either a common generalized approach or an empirically based tailored approach. We demonstrate that frequency distributions of landforms of varying ages can be used to develop local corrections that are more accurate than either global corrections or uncorrected estimates. Using generalized scenarios and a simulated case study based on empirical data on landform ages from the Coso Basin in the western Great Basin region, we illustrate the way in which landscape taphonomy predictably complicates “dates-as-data” approaches, propose and demonstrate a new method of empirically based correction, and explore the interpretive ramifications of ignoring or correcting for taphonomic bias.